
How to learn Russian? 5 best apps to master the language
Russian is a beautiful and complex language, spoken by millions around the world. And with the advent of language learning apps, it’s easier than ever to start picking up the basics of Russian. In this article, we’ll take a look at some of the best apps for learning Russian, discussing their features, pricing and overall effectiveness. Whether you’re a beginner just starting to explore the Russian alphabet or an experienced learner looking to take your language skills to the next level, there’s an app here for you. So, get ready to unlock the secrets of this rich and fascinating language and start your journey to fluency today!
1. Babbel
Babbel is a great app to learn Russian because it offers a comprehensive and personalized approach to language learning. With Babbel, you will have access to a wide range of interactive lessons that are tailored to your specific needs and learning style.
Babbel’s lessons are designed by experienced language teachers, so you can be sure that you are getting the most accurate and effective language instruction. The app also includes a variety of interactive exercises, quizzes, and games to help you practice what you’ve learned.
Web and smartphone application
One of the great things about Babbel is that it is available on a variety of platforms, including mobile devices and desktop computers. This means that you can learn Russian whenever and wherever you want. Whether you’re commuting to work, waiting for a friend, or just taking a break, you can always use Babbel to improve your language skills.
All language levels
Another advantage of Babbel is that it offers a wide range of language levels, from beginner to advanced. This means that whether you’re just starting to learn Russian or you’re looking to improve your existing skills, Babbel has something to offer.
Finally, Babbel is incredibly affordable, with a variety of subscription options to choose from. Whether you’re on a tight budget or looking for a more comprehensive program, Babbel has a pricing plan that will work for you.
Why this app?
- Comprehensive and personalized approach to language learning
- Available on a variety of platforms for anytime, anywhere learning
- Free subscription options
2. Mondly
Mondly is a good app to learn Russian because it offers a unique and immersive learning experience. With interactive lessons, real-life conversations, and a personalized daily progress tracker, Mondly helps you learn the language in a way that is both effective and engaging. Additionally, Mondly’s speech recognition technology allows you to practice your pronunciation and improve your speaking skills. With Mondly, you will not only learn the language, but also gain the confidence to speak it fluently.
Why this app?
- Interactive and immersive lessons
- Personalized daily progress tracker
- Speech recognition technology for improved pronunciation and speaking skills.
3. Memrise
Memrise is an innovative and effective way to learn Russian. With its unique approach to language learning, it combines engaging content, interactive exercises, and a personalized learning experience to help you achieve your language goals quickly and efficiently. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced learner, Memrise offers a wide range of resources and features to help you improve your vocabulary, grammar, and conversation skills. Plus, with its user-friendly interface and mobile app, you can learn on-the-go and make the most of your free time. With Memrise, you will be speaking Russian like a native in no time!
Why this app?
- Engaging content, interactive exercises and personalized learning experience
- Offers wide range of resources and features for different levels of learners
- User-friendly interface and mobile app for learning on-the-go.
4. Pimsleur
Pimsleur is a fantastic way to learn Russian because it is designed to teach you in the same way that you learned your first language. The program uses a unique method that focuses on teaching you the most important words and phrases first, and then building on them over time. This approach allows you to quickly gain a solid foundation in the language and become confident in your ability to speak and understand Russian. Additionally, Pimsleur’s audio-based lessons make it easy to fit learning into your busy schedule, whether you’re at home, on the go, or at the gym. With Pimsleur, you’ll be speaking Russian like a native in no time!
Why this app?
- Pimsleur offers a cost-effective way to learn Russian, with many of the lessons available for free or at a very low cost.
- The audio-based lessons make it easy to fit learning into a busy schedule and can be used while on the go.
- Pimsleur's method focuses on teaching the most important words and phrases first, allowing for a strong foundation in the language.
5. Rocket Languages
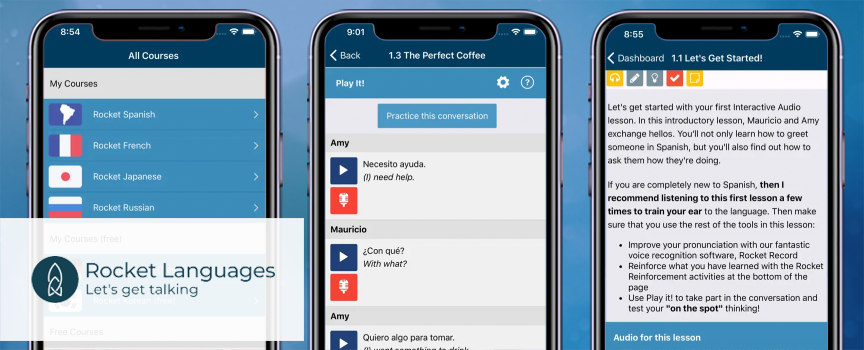
Rocket Languages is the ultimate solution for those looking to learn Russian. Not only does it offer a comprehensive curriculum that covers all aspects of the language, but it also utilizes interactive techniques such as speech recognition and conversation practice to ensure that you are able to actually use the language in real-life scenarios. Furthermore, the program’s flexibility allows you to learn at your own pace and on-the-go with mobile access. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to brush up on your Russian skills, Rocket Languages is the perfect tool to help you reach fluency.
Why this app?
- Affordable pricing with many features available for free
- Interactive techniques such as speech recognition and conversation practice
- Comprehensive curriculum that covers all aspects of the language
Russian language learning apps
How do these apps differ in terms of features and pricing?
Different apps offer a variety of features that can make a big difference in your learning experience. For example, some apps may include features such as:
- Interactive lessons and quizzes
- Speech recognition to help improve pronunciation
- Progress tracking and performance evaluation
- Offline access
- A comprehensive library of vocabulary, grammar, and idioms
For example, Duolingo offers interactive lessons and quizzes, speech recognition technology and progress tracking. Rosetta Stone, on the other hand, has a more immersive approach to teaching, using interactive images and speech recognition to help learners master the language, but it does not have a progress tracking feature.
Another example is Babbel, which focuses on practical, real-life situations and includes speech recognition to improve pronunciation, and offline access.
Pricing
Another key consideration when choosing a Russian learning app is pricing. Many apps offer free basic content, while others require a subscription or one-time purchase. Pricing may also vary depending on whether you’re purchasing a monthly, annual, or lifetime subscription.
For example, Duolingo is completely free, but to access some features such as progress tracking, you need to subscribe to their premium service. Rosetta Stone, on the other hand, offers a range of pricing options, from a monthly subscription to a lifetime purchase. The Babbel app offers a free trial then a subscription pricing model.
Which app is the most effective for beginner Russian learners?
There are several apps available that are specifically tailored for beginner learners of Russian. Here are a few examples:
Duolingo: Duolingo is a widely popular language learning app that is great for beginners. It uses a gamified approach to learning, with a series of lessons and exercises that cover the basics of Russian grammar, vocabulary, and sentence structure. The app also includes a feature called “Immersion,” which allows users to practice reading and listening to authentic Russian texts and audio.
Memrise: Memrise is another app that is well-suited for beginner learners of Russian. It offers a variety of engaging lessons and exercises, including flashcards and quizzes, that cover the fundamentals of the Russian language. One of the standout features of Memrise is its huge library of user-generated content, which includes audio recordings, videos, and images that make the learning experience more interesting and relatable.
Babbel: Babbel is a more traditional language learning app that focuses on building a solid foundation in Russian grammar, vocabulary and basic conversation. The app is designed to work through bite-sized lessons, which are focused on a specific aspect of the language, such as basic greetings, or basic grammar constructions, that are easy to grasp for beginners. The app provides grammar and vocabulary in context, and has interactive listening and speaking exercises.
Effectiveness
When it comes to determining which app is the most effective for beginner learners, it ultimately comes down to personal preference. Duolingo and Memrise are great options for those who prefer a more gamified and interactive approach, while Babbel is more traditional and effective for those who prefer more structured approach. However, all of the apps mentioned above have one thing in common which is effective, user-friendly and interactive way to learn Russian.
All of them have a great user interface and structure, that make it easy for beginners to understand and follow. The exercises and activities are designed in a way that makes it easy for beginners to understand and follow. They also provide feedback, explanations, and additional resources to help learners build a solid foundation in the language.
Examples of lessons
Here are a few examples of lessons or exercises you might find in these apps:
- Duolingo: A lesson on the Russian alphabet, where you have to match the Russian letters with the corresponding English letters.
- Memrise: A flashcard exercise that displays a Russian word and its English translation, followed by a multiple choice quiz to test your understanding.
- Babbel: A lesson that teaches you how to say “Hello” and “Goodbye” in Russian, with interactive speaking and listening exercises to reinforce your learning.
As a beginner learner, these apps provide an excellent introduction to the Russian language and will give you a solid foundation to build upon as you continue your journey to fluency.
Which app is the most effective for advanced learners?
There are several apps that are well-suited for advanced learners of Russian. Here are a few examples:
Duolingo
Duolingo is a popular language learning app that offers a comprehensive course for Russian. It’s great for advanced learners because it provides a wide range of exercises and activities that test listening, reading, writing, and speaking skills. It also offers a high degree of customization, so users can tailor the course to their specific needs and skill level.
Memrise
Memrise is another widely used language learning app that is well-suited for advanced learners of Russian. The app focuses on building vocabulary, grammar and conversation skills. It offers a variety of exercises that are designed to help learners internalize new words and phrases. It also offers an advanced course which gives more focus on grammar, idioms and more complex vocabulary.
FluentU
FluentU is a unique language learning app that uses real-world content, such as movie trailers, music videos, and news clips, to teach Russian. It’s great for advanced learners because it provides a wide range of authentic materials that are representative of the way Russian is spoken in real life. It also includes interactive captions, flashcards, quizzes and exercises that allows learners to practice their listening, reading, speaking and writing skills.
Lingodeer
Lingodeer is a language learning app that offers a structured course for Russian. The app is designed to help advanced learners internalize grammar rules, by providing clear explanations and plenty of examples, and also build a strong vocabulary. It also has a focus on conversation and listening skills and it’s known for its effective teaching methodologies.
How do these apps teach the Russian language and what methodologies do they use?
Methodologies
Language learning apps generally use one or a combination of several methodologies. Two of the most popular methodologies are:
- Audio-lingual method: This method focuses on drilling and repetition, using dialogues and audio exercises to help learners develop listening and speaking skills. This method also emphasizes on immediate feedback and correction.
- Task-based language teaching (TBLT) : It focuses on learners achieving real-life communicative tasks, such as ordering food, making appointments or giving directions. This method encourages the use of authentic materials.
Examples:
- Duolingo uses a combination of both methodologies, providing a mix of grammar exercises, listening practice, and vocabulary building. It includes immediate feedback and correction as well as real-life scenarios
- Rosetta Stone is an example of an app that focuses more on the audio-lingual method. It uses interactive images, real-life scenarios and dialogues to help learners develop their listening and speaking skills.
- Babbel is an app that uses the TBLT method, providing learners with real-life situations and practical vocabulary that they can immediately use in conversation.
How do these apps handle grammar, vocabulary and conversation teaching?
Grammar
Many of the apps for learning Russian place a strong emphasis on grammar. They often break down the grammar into manageable lessons and exercises, so that learners can focus on one aspect of the grammar at a time. For example, an app may have a lesson on the past tense, followed by exercises where learners practice conjugating verbs in the past tense. Some apps also include interactive games and quizzes to make grammar practice more engaging and fun.
Vocabulary
Vocabulary is another key component of language learning and many apps include a wide variety of vocabulary lists and flashcards to help learners expand their vocabulary. Often, these apps use flashcards with images and audio recordings to help learners associate new words with their meanings. Some apps also include vocabulary lists for specific topics, such as travel or business, so that learners can focus on vocabulary that is most relevant to them.
Conversation
Conversation is an essential part of language learning and many apps include conversation practice as part of their curriculum. Some apps include conversation lessons, where learners practice speaking with native speakers or with other learners. Some apps also have a feature where you can have a conversation with AI-based chatbot, which can help learners to have a more realistic conversation practice.
Additionally, Some apps also include interactive exercises and role-playing activities to help learners feel more comfortable with having real-life conversation. For example, an app may have a scenario where learners have to make a reservation at a restaurant in Russian or conduct a business meeting.
It’s worth noting that some apps may not be entirely focused on these three aspects, but the most of them try to cover them in a balance way. With this in mind, it’s important to have a look at the apps descriptions, features and reviews to have a better idea of what it’s focus.
Are there any free apps available to learn Russian?
Yes, there are several free apps available for learning Russian. These apps may offer a limited set of features or be ad-supported, but they can still be useful for getting started with the language. Here are a few examples of free Russian learning apps:
Duolingo
Duolingo is a popular language learning app that offers a free course for learning Russian. The course includes lessons on basic grammar, vocabulary, and sentence structure, with interactive exercises and games to help you practice what you’ve learned. The app also includes a built-in dictionary and a translation feature, which can be useful for looking up words and phrases. However, the free version might not include all features and content that a paid version would have.
Memrise
Memrise offers a free version of its app, which includes a variety of Russian language courses. These courses are created by a community of native speakers, and include lessons on grammar, vocabulary, and common expressions. The app includes a variety of interactive exercises and games to help you practice your new language skills.
AnkiApp
AnkiApp offers a flashcard-based approach to language learning, which can be especially effective for memorizing new vocabulary. The app offers a variety of user-created flashcard decks for Russian, including decks for common words, grammar, and conversation phrases. The app is free but with additional features are available with the paid version.
Are there any apps that have a specific focus, such as business Russian or Russian literature?
Business Russian
There are several apps that focus on teaching Russian specifically for business purposes. These apps typically offer lessons and exercises that focus on common business language and scenarios, such as conducting meetings, giving presentations, and negotiating deals. Some examples of apps that focus on business Russian include:
- “Learn Business Russian” which offers interactive exercises and dialogues, and it’s focus on specific vocabulary and language used in businesses.
- “RusBiznes” which is designed for those who want to improve their Russian for business purposes and it features business-specific vocabulary, idioms and expressions.
Russian literature
On the other hand, there are apps that focus on teaching the Russian language through the lens of literature. These apps often include lessons and exercises that feature famous works of Russian literature, such as the novels of Leo Tolstoy or the poetry of Alexander Pushkin. Some examples of apps that focus on Russian literature include:
- “Literary Russian” which aims to improve the learner’s vocabulary and grammar through reading and analyzing Russian literature.
- “Learn Russian with Tolstoy” which provides a unique approach to language learning through exploring Tolstoy’s literary masterpieces.
How do these apps incorporate speaking and listening practice?
Russian language learning apps typically incorporate speaking and listening practice by providing users with a variety of exercises and activities that are designed to help them improve their speaking and listening skills. Some common types of exercises and activities that these apps may include are:
- Pronunciation practice: Users can practice pronouncing individual sounds and words in Russian, and receive feedback on their pronunciation.
- Conversation practice: Users can engage in simulated conversations with native Russian speakers, and practice their speaking and listening skills in a realistic context.
- Vocabulary and grammar exercises: Users can practice new vocabulary and grammar structures by completing exercises such as multiple choice questions, fill-in-the-blank exercises, and sentence building activities.
- Audio exercises: Users can listen to recordings of native Russian speakers and practice their listening comprehension by answering questions or completing tasks based on what they heard.
- Speech recognition: Many apps uses this feature to give users the opportunity to speak and get feedback on their pronunciation, intonation and rhythm by recognizing their voice and comparing it to native speaker’s speech.
- Audio/Video recording and Playback: Users can record themselves speaking in Russian and then listen to the recordings to evaluate their own speaking skills and identify areas for improvement
Are there any apps that specifically target Russian culture?
Russian language learning apps that specifically target Russian culture aim to provide users with a comprehensive and immersive learning experience by incorporating elements of Russian culture into their language lessons. These apps typically feature content and exercises that focus on the language, customs, and traditions of Russia, helping users to understand the culture of the country they are learning in and build a deeper understanding of its people.
Learn Russian Culture and Language
One example of such app is “Learn Russian Culture and Language” that provides interactive lessons on a wide range of topics related to Russian culture, including traditional Russian cuisine, holidays and festivals, art, literature, and famous historical figures. Users can learn vocabulary and grammar while also gaining insight into the cultural context in which these words and structures are used. The app also includes interactive activities such as quizzes and flashcards, making the learning experience interactive and engaging.
Russian Language and Culture
Another example of app that targets Russian culture is “Russian Language and Culture”, which offers courses on various aspects of the culture, such as literature, folk tales, history and traditional songs, etc, as well as their language learning activities. The app also includes listening and reading exercises based on authentic Russian texts and materials such as short stories, newspaper articles and even movies. The user can also have access to a selection of Russian cultural news, that is updated periodically
In addition to these, there are other apps like “Survival Russian: Culture and Conversation” and “CultureAlley Russian Language Learning” that focus on teaching the language in a cultural context, providing users with a well-rounded understanding of both the language and the culture of Russia. These apps include interactive lessons, audio and video recordings, and other resources that aim to immerse the learner in the Russian culture and provide a more engaging and effective language learning experience.
What is the best way to learn Russian?
Are you looking to learn the Russian language but unsure of the best approach? Whether you’re a beginner or looking to improve your skills, there are many methods and resources available for learning Russian. From immersion and language classes, to tutoring and language exchange, the key to success is finding the method that works best for you. Below, we will explore the various ways to learn Russian and provide tips and resources to help you on your language learning journey.
Learning Russian by immersing yourself
When it comes to learning a new language, immersion is key. One of the best ways to immerse yourself in the Russian language is to surround yourself with it as much as possible. This can include listening to Russian music, watching Russian movies and TV shows, and reading Russian books and articles.
Russian music
Listening to Russian music can help you learn the language in several ways:
- Familiarize yourself with the rhythms and sounds of the language: Russian music can help you become familiar with the rhythms, intonations, and sounds of the language. This will make it easier for you to understand spoken Russian and to speak it yourself.
- Improve your vocabulary: Listening to Russian music can expose you to new words and phrases that you may not encounter in everyday conversation. This can help you expand your vocabulary and improve your understanding of the language.
- Learn colloquial language: Russian music often uses colloquial language and expressions, which can be difficult to find in textbooks or language classes. This can give you a more authentic understanding of how the language is used in real life.
- Cultural immersion: Listening to Russian music can also give you a glimpse into the culture and history of Russia, which can make the learning experience more enjoyable and engaging.
- Helps to improve your listening comprehension: As you listen to Russian music, you will be able to develop your listening comprehension skills, as well as your ability to understand spoken Russian in general.
How do you listen to Russian music to learn the language?
As a beginner learning Russian, there are several ways to listen to Russian music that can help you improve your language skills:
- Listen to music with lyrics: Listening to music with lyrics is one of the best ways to learn new vocabulary and grammar. Try to find songs with simple and easy-to-understand lyrics that focus on themes that you are interested in.
- Use lyrics translation: Many songs have lyrics translation available online. Try to find the lyrics of the song you are listening to and read along with the lyrics in Russian. This will help you to understand the meaning of the words and to improve your reading and listening skills.
- Repeat and sing along: Repeat the song you are listening to several times and try to sing along. This will help you to memorize the lyrics and to improve your pronunciation.
- Listen to music with a focus: Try to listen to music with a focus on certain aspects such as grammar or vocabulary. This can help you to identify specific areas that you need to work on.
- Use music to practice listening comprehension: As you listen to the music, try to understand the meaning of the lyrics and pay attention to the different sounds, intonations, and rhythms of the language.
Popular Russian songs to learn the language
Here are some popular Russian songs that are great for beginners to learn the language:
- “Песня о дружбе” (Song about Friendship) by Михаил Шуфутинский – This song is a classic and has simple lyrics that are easy to understand, making it a great starting point for beginners. The song is about the importance of friendship and has a catchy tune that is easy to sing along to.
- “Капли дождя” (Raindrops) by Леонид Руденко – This song has a upbeat and catchy tune and the lyrics are relatively simple. The song is about the feeling of falling in love and has a relatable theme that makes it easy to understand.
- “Пора домой” (Time to go home) by Алексей Чумаков – This song has a simple melody and lyrics that are easy to understand. The song is about the longing for home, it has a relatable theme that makes it easy to understand.
- “Любовь на расстоянии” (Long-distance love) by Юлианна Караулова – This song has a simple melody and lyrics that are easy to understand. The song is about the struggles of being in a long-distance relationship.
- “Полет над городом” (Flight over the city) by Владимир Кузьмин – This song has a simple melody and lyrics that are easy to understand. The song is about the desire to break free and fly away, it has relatable theme that makes it easy to understand.
Russian movies and TV shows
Watching Russian movies and TV series can help you learn the language in several ways:
- Listening comprehension: By watching Russian movies and TV series, you’ll have the opportunity to hear native speakers using the language in a variety of different contexts and situations. This will help you improve your listening comprehension skills and understand spoken Russian more easily.
- Vocabulary and grammar: As you watch, you’ll encounter new words and phrases that you may not have come across in your study materials. You’ll also see how grammar is used in context, which can help you understand how the language works in practice.
- Cultural context: Watching Russian movies and TV series can also give you an insight into the culture and customs of Russia, which can be helpful in understanding the language and communicating with native speakers.
- Subtitles: Watching movies or TV series with subtitles in Russian can help you learn the language in a more interactive way, as you can follow along with the subtitles, and learn new words, phrases, and grammar structures.
- Enjoyment: Watching movies and TV series in a language you’re learning can be a fun and enjoyable way to improve your language skills and make the learning process more engaging.
Here are a few popular Russian movies and TV shows that are suitable for beginners learning Russian:
Movies:
- “Лето” (Summer) – a coming-of-age film about a group of teenage friends during the summer of 1983 in Soviet Russia.
- “Давай поженимся!” (Let’s Get Married!) – a romantic comedy about a young couple who decide to get married, but their families and friends have different plans.
- “Прибытие” (Arrival) – a science fiction film about a team of scientists and an interpreter who must communicate with extraterrestrial visitors to learn why they have come to Earth.
TV Shows:
- “Дождь” (The Rain) – a crime drama about a detective who investigates a series of brutal murders in a small town.
- “След” (The Trace) – a crime thriller about a team of investigators who work to solve complex criminal cases.
- “Кухня” (The Kitchen) – a popular comedy-drama about the staff and customers of a restaurant in Moscow.
Russian books and articles
Reading Russian books and articles can help you learn the language in a number of ways.
- Vocabulary: By reading in Russian, you will encounter a wide range of vocabulary words and phrases that you may not have come across in other forms of immersion. This will help you to expand your vocabulary and become more proficient in the language.
- Grammar: Reading in Russian will also help you to improve your understanding of the language’s grammar. By reading a variety of texts, you will encounter different grammatical structures and forms, which will help you to better understand how the language works.
- Comprehension: Reading in Russian will help you to improve your comprehension skills. As you read, you will be exposed to different text structures, genres and writing styles, this will help you to understand the meaning of the words and phrases you encounter in the text.
- Cultural context: Reading Russian books and articles will also give you insight into Russian culture, customs, and society. This can help you to better understand the context of the language and improve your ability to use it in real-life situations.
- Writing skills: Reading in Russian also helps in improving your writing skills in the language as you are exposed to different writing styles and genres, this will help you to develop your own writing style and improve your ability to express yourself in Russian.
If you are a beginning Russian learner, it is best to start with texts that are written in a simple and straightforward language. This will help you to build your vocabulary and grammar skills, while also providing you with a sense of accomplishment as you read. Here are a few examples of Russian books and articles that are suitable for beginning learners:
- “Как закалялась сталь” by Aleksey Nikolayevich Tolstoy: This is a classic Soviet-era novel that tells the story of a young man who works in a steel factory. The language is simple and easy to understand, and the story provides a glimpse into the lives of ordinary Soviet citizens.
- “Война и мир” by Lev Tolstoy: This is a classic novel that tells the story of several aristocratic families in Russia during the Napoleonic Wars. Though it might be a bit challenging but it is a great way to improve your vocabulary and grammar skills.
- “Преступление и наказание” by Fyodor Dostoevsky: This is a classic novel that tells the story of a man who is driven to commit murder. The language is relatively simple, and the story provides a glimpse into the psychological motivations of the characters.
- Children’s books: Reading children’s books is a great way to start reading in Russian. They are usually written in simple language and contain illustrations that can help you understand the text better.
- News Articles from websites such as “РБК” or “Meduza” that cover current events and culture in Russia. They are written in a straightforward language and can provide you with a glimpse into the current state of the country.
Learn Russian by speaking with native speakers
Practice speaking Russian with native speakers as often as possible. This can be done through language exchange programs, language classes, or by finding conversation partners online. Not only will this help you improve your speaking skills, but it will also give you an opportunity to learn about the culture and customs of Russia.
Why speak with native speakers?
There are many benefits to speaking with native speakers when learning a new language. For one, it allows you to practice your speaking skills in a real-world context, which can help you become more fluent. Additionally, native speakers can provide you with accurate pronunciation and intonation, which are essential for sounding like a native speaker. Furthermore, speaking with native speakers gives you an opportunity to learn about the culture and customs of the country, which can deepen your understanding of the language and the people who speak it.
Ways to find and practice speaking with native speakers:
- Language Exchange Programs: Platforms such as Tandem, HelloTalk, and Speaky, provide an opportunity for language learners to connect with native speakers for language exchange. You can either have a conversation with native speakers or exchange written messages with them.
- Language Classes: Traditional language classes with native speakers can provide a more structured environment to practice speaking. Look for classes that focus on conversation, such as “Russian for conversation” or “Russian speaking club”
- Online Communities: There are many online communities such as “Russian learners” on social media platforms like Facebook, where you can connect with other language learners, and native speakers who can help you with your speaking skills.
- Conversation Partners: Look for conversation partners in your local area, either through language schools, community centers, or online groups. This will give you an opportunity to practice speaking in person, and also to learn more about the culture and customs of Russia.
- Traveling to Russia: One of the best ways to immerse yourself in the language and culture of Russia is to travel to the country. This will give you the opportunity to speak with native speakers in a real-world context, and experience the culture firsthand.
Mastering Russian Grammar and Vocabulary
Grammar and vocabulary are the building blocks of any language, and mastering them is essential for becoming fluent in Russian. While immersion in the language and speaking with native speakers are important for learning, practicing grammar and vocabulary is crucial for developing a solid foundation in the language. In this article, we will discuss the importance of practice and resources for mastering Russian grammar and vocabulary, and provide examples of ways to practice and resources to use.
Why practice grammar and vocabulary?
Practicing grammar and vocabulary is essential for solidifying your understanding of the language. Without practice, it can be easy to forget new words and grammar rules, and to make mistakes when speaking or writing. Additionally, practicing grammar and vocabulary allows you to focus on specific areas of the language that may be challenging for you, such as verb conjugations or word order.
Ways to practice grammar and vocabulary:
- Language Learning Apps: Duolingo, Rosetta Stone, and Babbel are all popular apps that can help you practice grammar and vocabulary. These apps offer interactive lessons, quizzes, and games to make learning fun and engaging.
- Textbooks: Traditional textbooks such as “Russian Grammar in Context” or “Complete Russian: The Basics” provide detailed explanations of grammar rules and exercises for practice.
- Flashcards: Creating flashcards with Russian words and phrases can be an effective way to practice vocabulary. You can use physical flashcards, or digital ones using apps like Anki.
- Language Learning Websites: Websites such as RussianPod101, Lingoda, and LiveMocha offer a variety of resources including grammar lessons, vocabulary lists, and practice exercises for learners at all levels.
- Practice with native speakers: As you practice grammar and vocabulary with native speakers, you will get instant feedback, and also learn about the culture and customs of the country.
For a more in-depth understanding of Russian grammar, be sure to reference the grammar chapter in this article.
Immerse Yourself in Russian Culture
Learning a new language is not just about mastering grammar and vocabulary, it’s also about understanding the culture and customs of the people who speak it. When it comes to Russian culture, there is a rich and diverse history to discover, from traditional customs to modern art and cuisine. Here are five ways to immerse yourself in Russian culture and gain a deeper understanding of the country and its people.
Travel to Russia
One of the best ways to immerse yourself in Russian culture is to visit the country itself. From the historic cities of Moscow and St. Petersburg to the natural beauty of Siberia and the Far East, there is something for everyone in Russia. While traveling, take the opportunity to experience traditional Russian customs, such as visiting a banya (a traditional Russian sauna) or trying local dishes like borscht and pelmeni.
Attend a Cultural Event
Russia is renowned for its rich cultural heritage, and there are many ways to experience it. From ballet and opera to classical music and theater, there are many cultural events to choose from. One of the most popular events is the annual “Golden Mask” Festival, where Russia’s best theater productions are showcased.
Explore Russian Art
Russia has a long history of artistic excellence, from the colorful onion domes of St. Basil’s Cathedral to the masterpieces of the Hermitage Museum. In addition to visiting museums and galleries, you can also explore the street art scene in Moscow and St. Petersburg.
Try Russian Cuisine
Russian cuisine is hearty and delicious, and it’s a great way to immerse yourself in the culture. From traditional dishes like beef stroganoff and blini to modern interpretations of classic recipes, there is something for everyone. For a truly authentic experience, try visiting a traditional Russian restaurant or café, or attend a “zakuski” (a traditional Russian feast)
Learn About Russian Literature
Russia has a rich literary tradition, from the classic novels of Leo Tolstoy and Fyodor Dostoevsky to the poetry of Alexander Pushkin and Anna Akhmatova. Reading Russian literature will give you a deeper understanding of the country’s culture, history, and people.
Taking Russian classes
Physical classes
One of the most effective ways to learn a language is through physical classes, where you can learn from a qualified teacher and have the opportunity to practice speaking and listening with other students. Russian is no exception and taking physical classes can be a great way to improve your language skills.
Benefits of physical classes:
- Personalized instruction: Having a teacher who can provide guidance and feedback on your progress can help you identify and overcome any challenges you may be facing.
- Interaction with other students: Physical classes provide an opportunity to interact with other students who are also learning the language. This can help you practice speaking and listening skills, and you may even make some new friends in the process.
- Structured learning: Physical classes follow a structured curriculum, which can help you stay on track and make steady progress.
- Access to resources: A teacher may have access to resources such as textbooks, audio recordings, and worksheets, which can be beneficial for your learning.
- Cultural awareness: Physical classes can provide you with an understanding of the Russian culture, which can be helpful in understanding and communicating with native speakers.
How to find the right class:
- Look for a qualified teacher: Make sure the teacher is a native Russian speaker with a teaching qualification, or has experience teaching Russian as a second language.
- Consider the class size: Smaller classes will provide more opportunities for personalized instruction and interaction with other students
- Determine the class schedule: Look for a class that fits into your schedule and can be attended on a regular basis.
- Check out the class materials: Ensure that the class will be using materials that are appropriate for your level and interests.
- Read reviews: Look for reviews of the class or teacher to get a sense of what to expect and if the class is a good fit for you.
Online classes
Online Russian classes are a convenient and flexible way to learn the language. With the right approach, you can make significant progress in your Russian language skills by taking online classes. Below, we’ll explore the benefits of online classes, the different types of classes available, and tips for getting the most out of your online learning experience.
Benefits of Online Russian Classes
- Convenience: Online classes can be taken from the comfort of your own home, at your own pace and schedule.
- Flexibility: Many online classes offer a variety of scheduling options, so you can find a class that fits your schedule.
- Variety: There are many different types of online classes available, from live classes with a teacher to self-paced classes and video lessons.
- Cost-effective: Online classes are often more affordable than in-person classes.
Types of Online Russian Classes
- Live classes: These classes are taught by a teacher in real-time, and offer the opportunity for interaction with the teacher and other students.
- Self-paced classes: These classes offer pre-recorded lessons that you can complete at your own pace.
- Video lessons: These classes consist of video lessons on specific topics, such as grammar or vocabulary.
- Tutoring: Online one-on-one tutoring can be a great way to get personalized instruction and feedback.
Tips for Getting the Most Out of Your Online Russian Classes
- Set a schedule: To make the most of your online classes, it’s important to set a schedule and stick to it.
- Practice regularly: Regular practice is essential for making progress in your language skills.
- Find a study partner: Finding someone to study with can make the learning experience more enjoyable and can also help you stay accountable.
- Take advantage of resources: Many online classes offer additional resources, such as quizzes, flashcards, and additional reading materials.
- Use the language outside of class: Try to use the language in real-life situations, such as watching Russian movies, reading Russian books, and speaking with native speakers.
Language exchange
One effective method for learning Russian is through language exchange. A language exchange is a partnership between a native Russian speaker and a non-native speaker of Russian, in which they help each other learn the other’s language. In this article, we will discuss the benefits of language exchange, how to find a language exchange partner, and how to make the most of your language exchange experience.
Benefits of Language Exchange
- Real-life practice: The most obvious benefit of language exchange is the opportunity to practice speaking and listening to the language in real-life situations.
- Cultural understanding: By communicating with a native Russian speaker, you will also learn about the culture and customs of Russia, which can help you understand the language better.
- Cost-effective: Unlike traditional language classes, language exchange is free.
- Flexibility: With a language exchange, you can set your own schedule and work on the areas of the language that you need to improve.
Finding a Language Exchange Partner
- Online language exchange platforms: There are many websites and apps that connect language learners with native speakers, such as Tandem, HelloTalk, and ConversationExchange.
- Social media: You can also use social media platforms to find a language exchange partner. Try searching for language exchange groups on Facebook or language exchange partners on Twitter.
- In-person: If you are living in a Russian-speaking country, you can also find a language exchange partner through in-person meetups or language exchange events.
Making the Most of Your Language Exchange Experience
- Set goals: Before you begin your language exchange, it’s important to set specific goals for what you want to achieve. This will help you stay focused during your conversations.
- Be patient: Remember that learning a new language takes time, and you will make mistakes. Be patient with yourself and your language exchange partner.
- Practice regularly: The more you practice, the faster you will improve. Try to have at least one conversation with your language exchange partner each week.
- Use different resources: In addition to speaking with your language exchange partner, take advantage of other resources such as language learning apps and podcasts to supplement your learning.
How long does it take to learn Russian?
The amount of time it takes to learn Russian can vary depending on several factors, such as the individual’s prior language learning experience, the amount of time they dedicate to studying, and the methods they use to learn.
Basic proficiency
On average, it is estimated that it takes around 600-750 hours of study to reach a basic level of proficiency in Russian. This translates to around 24 weeks of study, assuming a student studies for around 25 hours per week.
If you are a complete beginner, it might take you around 6-12 months to achieve a basic level of proficiency in Russian. This will allow you to have basic conversations, understand simple texts and navigate in Russian-speaking environment.
Fluent Russian
However, if you’re determined to become fluent in Russian, it will take much longer, around 2-3 years of consistent study and practice.
It’s important to note that the time it takes to learn Russian also depends on the learner’s goals and how they plan to use the language. If you only need to learn a few key phrases for a short trip, for example, you can likely achieve that in a much shorter amount of time.
Here is a table comparing different aspects of Russian to other similar languages, with a rating of how difficult it is to learn:
| Language | Vocabulary | Grammar | Pronunciation | Writing system | Difficulty level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Russian | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Hard | Moderate |
| Polish | Easy | Moderate | Easy | Easy | Easy |
| Ukrainian | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Hard | Moderate |
| Bulgarian | Moderate | Moderate | Easy | Hard | Moderate |
| Czech | Easy | Easy | Easy | Easy | Easy |
| Slovak | Easy | Easy | Easy | Easy | Easy |
| Serbian | Moderate | Moderate | Easy | Hard | Moderate |
| Croatian | Easy | Easy | Easy | Easy | Easy |
| Slovenian | Easy | Easy | Easy | Easy | Easy |
| Belarusian | Moderate | Moderate | Easy | Hard | Moderate |
The basics of learning Russian
Russian alphabet
When learning Russian, one of the first and most important steps is to familiarize yourself with the Russian alphabet. Also known as the Cyrillic alphabet, it consists of 33 letters and is used not only in Russia, but also in other countries such as Ukraine, Belarus, and Kazakhstan. Understanding the alphabet is crucial for being able to read and write in Russian, as well as for proper pronunciation.
The Cyrillic Alphabet
The Russian alphabet is based on the Cyrillic alphabet, which was invented in the 9th century by two Byzantine monks, Saint Cyril and Saint Methodius. The alphabet was originally designed to write the Slavic languages and has been adapted over time to write other languages as well. The modern Russian alphabet consists of 33 letters, 21 of which are consonants and 12 are vowels.
Similarities and Differences with the Latin Alphabet
For English speakers, some letters in the Russian alphabet may look similar to those in the Latin alphabet, such as “A”, “K”, “M”, and “O”. However, there are also many letters that look quite different and may take some getting used to. For example, the letter “В” (ve) looks like a Latin “B” but it is pronounced like “V”, and the letter “Р” (er) looks like a Latin “P” but it is pronounced like “R”.
Another important difference to note is that Russian is written in cursive, which means that letters are connected to each other when written. This means that the printed and written forms of letters may look different. It’s essential to practice writing the letters in cursive to get used to the different forms.
Pronunciation
Proper pronunciation is essential when learning any language, and the Russian alphabet is no exception. Although some letters may look similar to their Latin counterparts, they are often pronounced differently. It’s important to pay attention to the pronunciation of each letter and practice until you can say them correctly.
Listening to native speakers and imitating their pronunciation is a great way to improve your skills. There are also a variety of online resources such as videos, audio recordings, and apps that can help you with this.
Memorizing the Alphabet
Memorizing the Russian alphabet can seem daunting at first, but there are several ways to make it easier. One popular method is to use flashcards or apps that allow you to see the letter, hear its pronunciation, and practice writing it. Another method is to create mnemonics, or simple memory aids, to help you remember the letters.
It’s also essential to practice writing the letters by hand. This will help you to become more familiar with the different forms of the letters and make it easier for you to recognize them when you see them written.
| Cyrillic | Latin | Pronunciation | Example Word |
|---|---|---|---|
| А | A | ah | Апельсин (a-pel-sin) – Orange |
| Б | B | beh | Банан (ba-nan) – Banana |
| В | V | vye | Вода (va-da) – Water |
| Г | G | geh | Газ (gaz) – Gas |
| Д | D | deh | Дом (dom) – House |
| Е | E | ye | Елка (el-ka) – Christmas tree |
| Ё | Yo | yo | Ёлка (yol-ka) – Christmas tree |
| Ж | Zh | zhah | Жизнь (zhizn’) – Life |
| З | Z | zeh | Замок (zamok) – Castle |
| И | I | ee | Игрушка (ee-gru-shka) – Toy |
| Й | Y | ee kratkoye | Йогурт (ee-yogurt) – Yogurt |
| К | K | kah | Книга (knee-ga) – Book |
| Л | L | el | Лес (les) – Forest |
| М | M | em | Машина (ma-shin-a) – Car |
| Н | N | en | Нос (nos) – Nose |
| О | O | o | Окно (ok-no) – Window |
| П | P | peh | Пальто (pal’-to) – Coat |
| Р | R | er | Ручка (ruch-ka) – Pen |
| С | S | es | Солнце (solnce) – Sun |
| Т | T | teh | Телефон (te-le-fon) – Telephone |
| У | U | u | Утро (ut-ro) – Morning |
| Ф | F | ef | Футбол (foot-bol) – Football |
| Х | Kh | hah | Холод (kholod) – Cold |
| Ц | Ts | tseh | Цветок (tse-vot-ok) – Flower |
| Ч | Ch | cheh | Чай (chay) – Tea |
| Ш | Sh | shah | Школа (shko-la) – School |
| Щ | Shch | shcheh | Щекотка (shche-kat-ka) – Sneeze |
| Ъ | Hard Sign | – | Ъгли (ug-li) – Angles |
| Ы | Y | ee | Ы |
| Ь | Soft Sign | – | Ьело (belo) – White |
| Э | E | ye | Электричество (ye-lek-trees-tvo) – Electricity |
| Ю | Yu | yu | Юбка (yub-ka) – Skirt |
| Я | Ya | ya | Яблоко (yab-lo-ko) – Apple |
Russian Grammar
Russian grammar is a complex and fascinating aspect of the language. It is characterized by a rich system of inflections, which are used to indicate the grammatical function of words in a sentence. These inflections include changes in nouns, adjectives, pronouns, and verbs, and are used to indicate things like gender, number, case, tense, aspect, and voice. Additionally, Russian has a complex system of word order and special constructions, such as the use of the genitive case, the imperative, and the participle.
Differences between English and Russian language
| Feature | Russian | English |
|---|---|---|
| Alphabet | Cyrillic | Latin |
| Grammatical Cases | 6 (nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, instrumental, prepositional) | 2-3 (nominative, genitive, oblique) |
| Tense | Aspect (perfective/imperfective) | Tense (present, past, future) |
| Gender | 3 (masculine, feminine, neuter) | 2 (personal pronoun have only) |
| Word Order | Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) | Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) |
Nouns and noun declensions
In Russian, nouns have three genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), and they can be singular or plural. The gender and number of a noun determine the form of the article and adjectives that modify it.
Gender of Nouns
The gender of a noun can usually be determined by its ending, but there are many exceptions to this rule. For example, nouns ending in -a are typically feminine, but nouns ending in -о can be either masculine or neuter. Some nouns have no clear rule for determining their gender and must be memorized.
Number of Nouns
Nouns in Russian have two forms, singular and plural. The plural form of a noun can usually be determined by its ending, but there are also many exceptions to this rule. For example, nouns ending in -а or -я are typically plural, but nouns ending in -ь can be either singular or plural.
Declensions of Nouns
The case of a noun determines its grammatical function in a sentence. There are six cases in Russian: nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, instrumental, and prepositional. The ending of a noun changes depending on the case and number.
Nouns are declined by matching the ending of the noun with the ending of the article and/or adjective, depending on the gender and number. It’s a complex topic, but with practice it will become clearer.
Pronouns
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are used to indicate the person and number of the subject of a sentence. Russian has six personal pronouns: я (I), ты (you, informal singular), он/она/оно (he/she/it), мы (we), вы (you, formal or plural), они (they). They are inflected for case, which means that they change form depending on their grammatical role in the sentence.
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns indicate possession or belonging. They agree in gender, number, and case with the noun they modify. In Russian, possessive pronouns are formed by adding a suffix to the corresponding personal pronoun. For example, “my” is мой (moy) for masculine nouns, моя (moya) for feminine nouns, and мое (moye) for neuter nouns.
Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and object of a verb refer to the same person or thing. In Russian, reflexive pronouns are formed by adding the suffix -ся (sya) to the corresponding personal pronoun. For example, “I wash myself” is я моюсь (ya moyus’)
Examples
- Я люблю тебя (I love you)
- Он видит ее (He sees her)
- Мы покупаем свою квартиру (We’re buying our apartment)
- Они говорят о себе (They talk about themselves)
Practice exercises:
- Rewrite the following sentences replacing the personal pronoun with a possessive pronoun
- Translate the following sentences into Russian using reflexive pronoun
Cultural Note
It is important to note that in Russian language, the formal and informal forms of “you” are used differently than in English, and it’s important to use the correct form in order to show respect to the person you’re speaking to.
Adjectives in Russian
Russian adjectives agree in gender, number, and case with the nouns they modify. In this section, we’ll discuss the forms of Russian adjectives and their usage.
Short and Long Forms
Russian adjectives have two forms: the short form and the long form. The short form is used before a noun, while the long form is used after a verb or preposition.
For example, consider the adjective “красный” (red). The short form is “красный,” while the long form is “красный.”
- Красный дом (red house)
- Дом красный (the house is red)
Agreement with Nouns
As mentioned, Russian adjectives agree in gender, number, and case with the nouns they modify.
For example, consider the adjective “старый” (old). If it modifies a masculine noun in the nominative case, it would be “старый” (old). If it modifies a feminine noun in the accusative case, it would be “старую” (old).
- Старый дом (old house)
- Я вижу старую книгу (I see an old book)
Usage
Russian adjectives can be used in a variety of ways, including as predicate adjectives, as attributes and as subject complements.
For example, “Этот дом красивый” (This house is beautiful) Here “красивый” is used as a predicate adjective.
- Я вижу красивый дом (I see a beautiful house)
- Here, “красивый” is used as an attribute.
Adjectives can also be used in the form of subject complements, as in “Дом красивый” (The house is beautiful)
Practice exercises
Translate the following sentences into Russian:
- The red car
- The old man
- I see a beautiful flower
Identify the adjective and the noun it modifies in the following sentence: “Я вижу красивый дом” (I see a beautiful house)
Verbs
Conjugation
In Russian, verbs have six forms, called “persons,” which include the first, second, and third person singular and plural. The conjugation of a verb depends on the person of the subject and the tense of the verb. The present tense, for example, has a different conjugation for each person.
Aspect
Russian verbs have two aspects: the perfective and the imperfective aspect. The perfective aspect indicates a completed action, while the imperfective aspect indicates an ongoing or repeated action. The aspect of a verb can change the meaning of a sentence.
Voice
Russian verbs also have two voices: the active and the passive voice. The active voice indicates that the subject of the sentence is performing the action, while the passive voice indicates that the subject is the recipient of the action. The voice of a verb can change the emphasis of a sentence.
Examples and exercises
Here are some examples of verb conjugation, aspect, and voice:
- Present tense, first person singular: Я говорю (I speak)
- Past tense, imperfective aspect: Я говорил (I was speaking)
- Future tense, perfective aspect: Я буду говорить (I will speak)
- Active voice: Он пишет книгу (He is writing a book
- Passive voice: Книга пишется им (The book is being written by him)
Exercise: Conjugate the verb “брать” (to take) in the present tense, imperfective aspect, active voice for all six persons.
Answers:
- Я беру (I take)
- Ты берёшь (You take)
- Он/Она/Оно берёт (He/She/It takes)
- Мы берём (We take)
- Вы берёте (You take)
- Они берут (They take)
Adverbs
Adverbs are words that describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They indicate how, when, where, or to what degree an action is performed.
Usage of Adverbs
Adverbs in Russian can be placed before, after, or between the verb and its object. The position of the adverb depends on the emphasis that the speaker wants to put on it. For example, “Я очень хорошо говорю по-русски” (I speak Russian very well) the adverb “очень” (very) is placed before the adjective “хорошо” (well) to indicate that the speaker speaks very well.
Adverb forms
Unlike adjectives, adverbs in Russian do not change form to agree with the noun or pronoun they modify. They remain the same, regardless of whether the verb is in singular or plural form. The same applies to the gender and the case of the noun.
Examples
Here are some examples of adverbs in Russian:
- Быстро (quickly)
- Внимательно (attentively)
- Громко (loudly)
- Долго (for a long time)
- Медленно (slowly)
Practice
Here is an exercise to practice using adverbs in Russian:
Translate the following sentence into Russian: “He speaks quietly.”
Answer: Он говорит тихо.
Prepositions
In Russian, prepositions are words that indicate the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. They indicate the direction, location, or time of an action or event. Understanding prepositions is important for understanding the meaning of a sentence.
Types of Prepositions
There are several types of prepositions in Russian, including:
- Directional prepositions, indicating the direction of an action, such as “в” (to) and “из” (from)
- Locative prepositions, indicating the location of an action, such as “на” (on) and “под” (under)
- Temporal prepositions, indicating the time of an action, such as “в” (in) and “за” (before)
Cases Governed by Prepositions
Prepositions govern the case of the noun or pronoun that follows them. For example, the preposition “в” (in) governs the accusative case, while the preposition “на” (on) governs the prepositional case. It is important to know which case a preposition governs in order to use it correctly.
Common Prepositions
Here are some common prepositions in Russian and their meanings:
- “в” (in, into): as in “в комнате” (in the room)
- “на” (on, upon): as in “на столе” (on the table)
- “под” (under): as in “под столом” (under the table)
- “с” (with): as in “с друзьями” (with friends)
- “без” (without): as in “без сахара” (without sugar)
- “о” (about): as in “о книге” (about the book)
It’s important to note that some prepositions have multiple meanings, depending on the context. It’s important to practice and read a lot to get a better understanding of the usage of prepositions.
Word order
The basic word order in Russian is subject-verb-object (SVO), similar to English. However, word order can be rearranged for emphasis or to indicate a specific meaning. For example, “Ivan reads the book” can be rephrased as “The book, Ivan reads” to put emphasis on the book.
Use of Emphasis
Emphasis in Russian can be achieved by placing the emphasized word or phrase in a different position within the sentence. For example, “Ivan, he reads the book” places emphasis on the subject, Ivan. It can also be achieved by using the particle “da” or “to” at the end of the sentence, indicating that the speaker is stressing the truth of the statement.
Comparison with English
It’s important to note that word order in Russian is more flexible than in English. In English, word order is crucial for understanding the meaning of a sentence, whereas in Russian, the case system provides more information about the grammatical function of the words in a sentence.
Syntax
Subordinate clauses
Russian has two types of subordinate clauses: dependent clauses introduced by a conjunction and clauses introduced by a relative pronoun. The conjunction “что” (that) is the most common conjunction used for introducing dependent clauses. For example:
“Я знаю, что ты сделал” (I know that you did).
Relative clauses
Relative clauses are introduced by a relative pronoun, such as “кто” (who), “что” (that), or “который” (which). These clauses provide additional information about the noun or pronoun they modify. For example:
“Машина, которую я купил, очень дорогая” (The car that I bought is very expensive).
Word order in subordinate and relative clauses
In subordinate and relative clauses, the word order is generally subject-verb-object. However, the word order may be rearranged for emphasis or to indicate a specific meaning.
Special constructions
In some cases, subordinate and relative clauses can also be introduced by a participle or an infinitive. These constructions provide additional information about the action or state described in the main clause.
Example:
“Я видел мужчину, курящего сигарету” (I saw a man smoking a cigarette).
The participle “курящего” (smoking) is used here to describe the man in the relative clause.
Exercises
- Complete the following sentence using the appropriate conjunction or relative pronoun: “Я не знаю ____________ ты говоришь” (I don’t know what you are talking about).
- Provide a translation for the following sentence: “Дом, который мы купили, очень красивый” (The house that we bought is very beautiful).
- Rewrite the following sentence, changing the word order for emphasis: “Я видел мужчину курящего сигарету” (I saw a man smoking a cigarette).
Russian vocabulary
Russian vocabulary is unique in its use of six grammatical cases, which change the endings of nouns, adjectives, and pronouns depending on their role in a sentence. This feature allows for more precise and nuanced expression, but also makes Russian grammar more complex than that of English. Additionally, Russian has a large number of loanwords from French, German, and other languages, which adds to its lexical diversity.
Russian vocabulary compared to English
Compared to English, Russian has a greater number of synonyms for certain words and concepts, which can make it more expressive and poetic. However, this can also make it more challenging for learners to master. Russian also has a complex system of verb conjugations, which can be difficult for English speakers to navigate.
Basic words and phrases for everyday communication
Greeting and Introducing Yourself
Привет (pree-vyet) – Hello
Как дела? (kak dyel-la) – How are you?
Меня зовут… (mee-nya za-voot) – My name is…
Рад вас видеть (rad vas vee-dyet) – Nice to meet you
Asking for Directions
Где… (gdy) – Where…
Как добраться до… (kak do-brat-sya do) – How to get to…
В каком направлении… (v kakom napra-vle-neey) – In which direction…
Сколько километров? (skol-ka ki-lo-me-trov) – How many kilometers?
Ordering Food
Что вы посоветуете? (shto vy po-sa-ve-tye-tye) – What do you recommend?
Я хочу… (ya ho-choo) – I want…
Я не ем… (ya ne yem) – I don’t eat…
Можно со сливками? (mozh-na so slev-kam) – Can I have it with cream?
Shopping
Сколько это стоит? (skol-ka e-to stoy-it) – How much does it cost?
Я хочу купить… (ya ho-choo koo-pit) – I want to buy…
Где находится… (gdy na-ho-dits-ya) – Where is…
Я беру это (ya beru e-to) – I’ll take this
Slang and colloquial expressions
Slang and colloquial expressions are words and phrases that are commonly used in informal situations. They are often seen as informal, casual, and even vulgar, but they are an integral part of the language and culture. They can help you understand the culture better, and make you sound more like a native speaker.
Russian slang words
Slang words are informal words that are often used to replace formal words. They can be used to express emotions, feelings, and attitudes. Some examples of popular slang words in Russia include:
Братан (bratan) – this word is used to address a friend, similar to the English word “dude” or “bro.”
Давай (davay) – this word is used to encourage someone to do something, similar to the English phrase “let’s go.”
Просто (prosto) – this word can be used to express surprise, similar to the English phrase “seriously?”
Colloquial expressions
Colloquial expressions are phrases that are commonly used in informal situations. They can be used to express emotions, feelings, and attitudes. Some examples of popular colloquial expressions in Russia include:
На своей коже (na svoyey kozhe) – this phrase is used to express personal experience, similar to the English phrase “on my own skin.”
На всякий случай (na vsyakiy slucha) – this phrase is used to express caution, similar to the English phrase “just in case.”
Все как всегда (vse kak vsegda) – this phrase is used to express the status quo, similar to the English phrase “as always.”
False friends in Russian
False friends, also known as false cognates, are words in different languages that are similar in form and meaning, but have different meanings. They can cause confusion for learners of a new language and may lead to mistranslation. Russian is no exception and has several false friends that can trip up English speakers.
One example of a false friend in Russian vocabulary is the word “банк” (bank), which in English refers to a financial institution, whereas in Russian, it refers to a bench. Another example is the word “бабушка” (babushka), which in English refers to a grandmother, but in Russian, it means an old woman.
Another example is “гость” (gost) which means a guest in English but in Russian it means host. “Студент” (student) which in English refers to someone who is studying at a college or university, but in Russian, it refers to a schoolboy or a schoolgirl.
Additionally, the word “парк” (park) in English refers to a public space with trees, grass, and other landscaping, but in Russian, it refers to a parking lot.
It’s important for English speakers learning Russian to be aware of these false friends and to pay close attention to the context in which words are used to avoid confusion. It’s also good to practice with native speakers or with the help of a teacher who can help you to understand the meaning of words and their usage in different situations.
Pronunciation in Russian
Russian pronunciation can be challenging for English speakers due to its unique alphabet and different sound system. The Russian alphabet, also known as the Cyrillic alphabet, contains 33 letters, some of which have no direct equivalent in the English alphabet. Additionally, Russian has a system of hard and soft consonants, which changes the pronunciation of the preceding vowel. Stress and accentuation also play a significant role in Russian pronunciation, as the emphasis on certain syllables can change the meaning of a word. Other important aspects of Russian pronunciation include vowel reduction and neutralization, commonly mispronounced sounds and words, and regional variations. To improve your Russian pronunciation, it is important to practice listening and speaking with native speakers, and to pay close attention to the nuances of the language.
| Russian Pronunciation | English Pronunciation |
|---|---|
| Hard and soft consonants | No hard and soft consonants |
| Vowel reduction and neutralization | Vowel sounds are usually pronounced clearly and consistently |
| Stress and accentuation | Stress on different syllables can change the meaning of a word |
| Pronunciation of the letter “o” | The letter “o” is pronounced as “a” in English |
| Pronunciation of the letter “e” | The letter “e” is pronounced as “ye” in English |
| Pronunciation of the letter “y” | The letter “y” is pronounced as “ee” in English |
| Pronunciation of the letter “x” | The letter “x” is pronounced as “h” in English |
Hard and soft consonants
In Russian, many consonants can be pronounced either “hard” or “soft” depending on the letters that follow them. A “hard” consonant is pronounced with the full force of the breath, while a “soft” consonant is pronounced more gently. The difference in pronunciation can change the meaning of a word.
For example, the letter “б” (b) is pronounced hard before a hard vowel (like “а” or “о”), and soft before a soft vowel (like “я” or “ё”). So “банк” (bank) is pronounced with a hard “б” sound, while “берег” (beach) is pronounced with a soft “б” sound.
Other examples of hard and soft consonants include: “г” (g) and “ж” (zh), “д” (d) and “з” (z), “к” (k) and “х” (kh), “т” (t) and “ц” (ts), “п” (p) and “ф” (f), and “с” (s) and “ш” (sh).
Stress and accentuation
In Russian, stress (or accent) is very important for proper pronunciation and can change the meaning of a word. Stress usually falls on the last syllable of a word, but it can also fall on the second-to-last syllable. Some examples of words with different stress patterns include:
- “гость” (guest) and “гости” (guests), where the stress falls on the last syllable in the singular form and the second-to-last syllable in the plural form.
- “река” (river) and “реку” (to/for a river), where the stress falls on the first syllable in the noun form and the second syllable in the prepositional form.
It’s important to learn the correct stress patterns for words, as it can change the meaning of a word. For example “Работать” (to work) and “работать” (to work on) both have different stress, and that’s the only difference between them.
Vowel reduction and neutralization
In Russian, certain vowels can change their sound depending on their position in a word and the surrounding sounds. This process is known as vowel reduction.
One example of vowel reduction is the sound “o” in the word “город” (gorod) which means “city”. The “o” in this word is pronounced as a more closed and less stressed sound, as compared to the “o” in the word “мотоцикл” (mototsikl) which means “motorcycle”.
Another example is the sound “e” in the word “белый” (belyi) which means “white”, which is pronounced as a more closed and less stressed sound, as compared to the “e” in the word “день” (den) which means “day”
Another aspect of vowel reduction is neutralization, which is when a vowel sound loses its distinct quality and becomes similar to another vowel sound. An example of this is the sound “a” in the word “час” (chas) which means “hour” and the sound “o” in the word “молоко” (moloko) which means “milk”, both of which are pronounced with a more closed sound and becomes similar to “o” in “мотоцикл” (mototsikl) which means “motorcycle”.
Tips for improving your Russian pronunciation
- Familiarize yourself with the Russian alphabet and its pronunciation. This will help you understand the sounds of the language and how they are represented in writing.
- Practice the different vowel and consonant sounds. Russian has several unique sounds that may be difficult for non-native speakers to produce, such as the “ё” sound or the “ж” sound.
- Pay attention to stress and accentuation. Russian words have different stress patterns, and placing stress on the wrong syllable can change the meaning of a word.
- Practice listening to native speakers and repeating what you hear. This will help you develop your ear for the language and improve your pronunciation.
- Record yourself speaking Russian and listen to the recording. This will allow you to hear any errors or areas where you need to improve.
- Take a Russian pronunciation course or work with a tutor. A professional can provide you with personalized instruction and feedback to help you improve your pronunciation.
- Watch Russian-language videos and movies. This will expose you to the natural rhythms, intonations and accent of native speakers and help you to get a sense of how to sound more like them.
- Practice regularly, Consistency is key when it comes to improving your pronunciation. Even just a few minutes of practice each day can make a big difference over time.
Learning Russian by studying Russian culture
Learning about Russian culture can greatly enhance your understanding and appreciation of the language. Here are a few reasons why:
- Cultural context helps to deepen understanding of language. Understanding the customs, traditions and values of a culture can give you a better understanding of the language, as well as the people who speak it.
- Vocabulary and idioms. Many words and phrases in any language have cultural connotations that cannot be fully understood without knowledge of the culture. Understanding the culture can help you understand the meaning and usage of these words and phrases.
- Improving communication and social interactions. Knowing about the culture will help you to navigate social situations, understand nonverbal cues and make more meaningful connections with native speakers.
- Appreciation and curiosity. Russian culture is rich and fascinating, and learning about it can help you to appreciate the language and culture more and be more curious about it.
- Business and professional. Understanding the culture can be beneficial for professionals, such as business people, who may interact with Russian-speaking clients, partners or colleagues.
- Travel. Knowing about the culture will make your travel experience more enjoyable and will help you to understand and appreciate the places you visit.
Russian literature and literary figures
Russian literature is renowned for its depth, complexity, and beauty. Understanding the works of famous Russian writers such as Pushkin, Dostoevsky, Tolstoy, and Chekhov can greatly enhance your understanding and appreciation of the Russian language. Here are a few ways in which studying Russian literature can help you learn the language:
- Vocabulary and grammar: Reading literature in a foreign language can help you expand your vocabulary and improve your grammar. Russian literature is written in a formal and elevated style, which can help you to learn more advanced vocabulary and grammar structures.
- Cultural context: Russian literature is deeply rooted in the country’s culture and history. Reading the works of famous Russian writers can give you a deeper understanding of the country’s customs, traditions, and values. This can help you to understand the language more fully and communicate more effectively with native speakers.
- Idiomatic expressions: Russian literature is full of idiomatic expressions, which can be difficult for non-native speakers to understand. Reading literature can help you to learn these expressions in context and understand how to use them correctly.
- Pronunciation: Reading literature can help you to improve your pronunciation. By reading the works of famous Russian writers, you can learn to hear and produce the sounds of the language more accurately.
- Appreciation: Reading literature can help you to appreciate the beauty and complexity of the Russian language. Understanding the works of famous Russian writers can give you a greater appreciation for the language and its rich literary tradition.
Russian art and architecture
Russian art and architecture can be helpful when learning the language for a few reasons.
- Vocabulary: Understanding the terminology used to describe art and architecture can help you expand your vocabulary and improve your ability to speak and understand the language.
- Cultural context: Russian art and architecture is deeply intertwined with the country’s history and culture. Understanding the historical and cultural context in which these works were created can give you a deeper understanding of the language and the people who speak it.
- Appreciation: Russian art and architecture is renowned for its beauty and historical significance. Appreciating these works can give you a greater appreciation for the culture and the language.
- Conversation topics: Knowing about Russian art and architecture can give you something interesting to talk about with native speakers and can help you to make more meaningful connections with them.
Russian music and dance
From classical compositions by Tchaikovsky and Rachmaninoff to the energetic rhythms of traditional folk dances, Russian music and dance have played an important role in the country’s culture.
Music and dance can play a significant role in helping you learn the language. Here are a few ways that studying Russian music and dance can aid your language learning:
- Vocabulary and idioms: Russian songs often include words and phrases that are not commonly used in everyday conversation. Learning these words through songs can make them easier to remember and understand.
- Pronunciation and intonation: Listening to native speakers sing or speak in songs can help you to develop your ear for the language and improve your own pronunciation and intonation.
- Cultural understanding: Russian music and dance can provide insight into the country’s culture and customs. Understanding the meaning and significance of different songs and dances can give you a deeper appreciation of the culture.
- Memorization: Many songs have catchy melodies and repetitive lyrics, which can make them easy to remember. By memorizing the lyrics to a Russian song, you can practice your vocabulary and grammar.
- Enjoyment: Learning a language can be challenging, but incorporating music and dance can make it more enjoyable. By listening to Russian music and watching Russian dance performances, you can have fun while learning the language.
Russian food and cuisine
Understanding traditional Russian dishes and ingredients can help you to appreciate the culture and in turn enhance your understanding of the language. Here’s how:
- Vocabulary: Understanding the names of traditional dishes and ingredients can help you to expand your vocabulary and improve your ability to communicate about food. For example, knowing that “борщ” (borshch) is a traditional beet soup, or that “пельмени” (pelmeni) are dumplings, will make it easier for you to understand and participate in conversations about food.
- Idiomatic expressions: Many idiomatic expressions in Russian are related to food and cuisine. For example, “жареный в масле” (zharényj v masle) which literally means “fried in oil” is used to describe a person who is successful, rich or well-off. Knowing this idiomatic expressions can help you understand and use them correctly.
- Social interactions: Knowing about traditional dishes and ingredients can also help you navigate social interactions. For example, if you know that “каша” (kasha) is a traditional porridge made from grains, you’ll know that it is often served as a breakfast food, and that it is considered to be a simple and humble dish.
- Appreciation: Understanding the diversity and richness of Russian cuisine can also help you to appreciate the culture more and be more curious about it. Russian cuisine has a wide range of flavors, textures, and ingredients that can be quite different than the ones you may be used to.
- Travel: Knowing about traditional dishes and ingredients can also make your travel experience more enjoyable, as you will be able to order food that you are familiar with or try new ones with more confidence
Russian holidays and festivals
Russian holidays and festivals are an important part of the culture and can be a valuable tool for learning the language. Here’s how:
- Vocabulary and expressions: Many holidays and festivals have specific words and expressions associated with them, such as “праздник” (holiday) or “праздничный” (festive). Understanding these words and how they are used in context can help you expand your vocabulary.
- Cultural context: Understanding the customs and traditions associated with holidays and festivals can give you a better understanding of the culture and the people who speak the language. For example, learning about the traditional Russian New Year’s celebration, “Новый год” (Novy God) can help you understand the importance of family, food and gift-giving in Russian culture.
- Cultural immersion: Participating in holidays and festivals, whether in Russia or in a Russian-speaking community, can give you a sense of immersion in the culture and help you to practice your language skills in a natural and authentic setting.
- Conversation topics: Holidays and festivals can be great conversation starters and a way to practice your speaking and listening skills. For example, you can talk about your own holiday traditions, ask about Russian traditions or exchange opinions about the festival.
- Understanding the context of the culture: Holidays and festivals are an important part of the culture, they can help you understand the cultural context of the language. For example, Learning about the Victory Day parade, “День Победы” (Den’ Pobedy) and its significance to the Russian people can give you a deeper understanding of the importance of military history in Russian culture and how it is reflected in the language.
Russian history
Russian history, can be an important aspect of learning the language as it can give you a better understanding of the country and its culture. Understanding the historical context of the language can help you to understand the language and the people who speak it in a deeper way. Here are a few examples of how understanding Russian history can help you learn the language:
- Vocabulary and idioms: Many words and phrases in the Russian language have historical connotations that cannot be fully understood without knowledge of the culture’s history. For example, understanding the history of the Soviet Union can help you understand the meaning and usage of words such as “Совет” (Council) and “Коммунист” (Communist).
- Literature and literary figures: Many of Russia’s most famous writers, such as Pushkin, Dostoevsky, and Tolstoy, have written about historical events and figures. Understanding the historical context of their works can give you a deeper understanding of the language and the culture.
- Social and political context: Many Russian words and phrases are related to political and social issues that have shaped the country’s history. Understanding the context of these words and phrases can help you to understand the language more deeply and communicate more effectively.
- Business and Professional context: Understanding the historical context of the country’s political, economic, and cultural development can help you to understand the current business and professional environment and make better decisions when dealing with Russian-speaking clients, partners, or colleagues.
- Travel context: Understanding the historical context of the country’s landmarks and tourist attractions can help you to appreciate and understand the places you visit and make the most of your travel experience.
Russian customs and etiquette
Russian customs and etiquette can be an important aspect of learning the language. Understanding the customs and etiquette of a culture can help you navigate social interactions and communicate more effectively.
- For example, in Russia it is customary to dress more formally for social events and business meetings than in some other cultures. Knowing this will help you to dress appropriately and make a good impression.
- Another example is the traditional art of toasting, in Russia it is common to make a toast before drinking, usually with vodka. Toasting is an important part of socializing and business interactions in Russia, so understanding the customs and etiquette surrounding toasting can help you to participate more effectively in these situations.
- Additionally, it is considered impolite to be late for an appointment, meeting or social event, so understanding the importance of punctuality in Russian culture can help you to avoid offending anyone.
In general, understanding the customs and etiquette of a culture can help you to navigate social interactions more easily and communicate more effectively. This can be especially important when learning a language, as it can help you to understand the nuances of the language in a cultural context. For example, when you understand that in Russia, people tend to be direct and to the point, and avoid small talk, you can use the right words or expressions to get straight to the point in a conversation or a business meeting.
Russian business culture
Russian Business culture is an important aspect of Russian culture to understand when learning the language, as it can have a significant impact on communication and social interactions in a professional setting. Here are a few ways in which understanding Russian business culture can help you learn the language:
- Vocabulary and idioms: The business world has its own set of terms and phrases that may not be covered in a general language course. Understanding these terms and phrases will help you to communicate more effectively in a professional setting.
- Social interactions and communication styles: Russians may have different communication styles and social norms in a professional setting compared to other cultures. Understanding these differences will help you to navigate professional interactions more smoothly.
- Negotiations and business etiquette: Russians may have different approaches to negotiations and business etiquette compared to other cultures. Understanding these differences will help you to make a better impression and be more successful in a professional setting.
- Networking and building relationships: Building relationships is an important aspect of doing business in Russia. Understanding the Russian approach to networking and relationship-building can help you to make valuable connections.
- Cultural sensitivity: Understanding the Russian business culture will help you to be more sensitive to cultural differences and avoid any potential misunderstandings or offense.
Examples:
- You are attending a meeting with Russian business partners, understanding their direct and assertive communication style, will help you to be prepared and not get caught off guard.
- If you are planning to do business in Russia, it’s important to understand that building relationships and trust is a key aspect of doing business in Russia, and showing respect and understanding towards their culture can help in that process.
- If you are negotiating with a Russian company, understanding their approach to negotiations and business etiquette, such as being punctual, can help you to make a better impression and be more successful in reaching an agreement.












